Human papillomavirus HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection. It’s very prevalent, with sexually active people getting diagnosed at some point in their lives. But how do you know you have HPV? Let’s discover the symptoms of Human papillomavirus (HPV) to understand them better and learn how to manage them and also how to prevent hpv human papillomavirus infections
What is HPV?
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is a common viral infection. This virus is primarily exposed through sexual contact in sexually active individuals. With over 100 types of strains of hpv, majority of strains of hpv can be cleared by your immune system, while certain high risk types can cause problems like cancer or hpv and genital warts. The HPV virus is transmitted primarily through skin-to-skin contact, often during sexual activity for genital hpv infection. It can spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, non-sexual skin-to-skin contact and vertically (mother to baby).
There are two main categories of HPV strains:
Low-risk HPV – these strains, such as HPV 6 and 11, can cause genital warts but rarely lead to cancer. Other low-risk stains can cause warts on hands and feet, such as plantar warts or flat warts.
Plantar warts and flat warts are not sexually transmitted infections. Genital warts, however, are a form of STD. Most infections with HPV can be cleared by your own body unless you have a weakened immune system.
High-risk HPV – these strains, particularly HPV 16 and 18, has an increased risk of certain cancers, such as cervical, anal, penile, vaginal, vulvar, and oropharyngeal (throat) cancers. These high risks can be prevented with HPV vaccines and should be regularly screened with regular pap tests.
Do I Have HPV Symptoms?
Most people with HPV do not experience any symptoms. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential symptoms that HPV can cause.
When Do HPV Symptoms Appear?
Symptoms can appear anywhere from weeks to months or even years after initial HPV infection. However, it varies depending on the individual and the specific strain of HPV.
Common HPV Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms associated with HPV infections include:
Genital warts: Small, flesh-coloured growths, bumps, or cauliflower-shaped warts in the genital area. They can appear as raised bumps which are painless.
Common warts: Small, rough, grainy skin growths that typically appear on the fingers, around the nails, or on the hands. These are harmless growths.
Plantar warts: Warts located on the soles of feet.
Flat warts: Small, smooth, flat-topped growths that can appear commonly on the face, neck, hands, or knees.
Symptoms in Women
Women with HPV may experience symptoms such as:
Genital warts on the vulva, vagina, cervix, or anus
Abnormal cells of the cervix found during a pap smear
Oral and throat lesions
Symptoms in Men
Men with HPV may experience:
Visible warts on the scrotum or anus
Oral and throat lesions
Penile warts
Less Common HPV Symptoms
While the majority of HPV infections remain asymptomatic or cause only mild symptoms such as warts, certain strains of HPV, particularly the high-risk ones, can lead to more serious health issues. These strains are associated with the development of several types of cancers, although it is important to note that HPV-related outcomes are rare and usually follow a prolonged period of persistent infection.
Cervical Cancers: High-risk HPV strains, such as types 16 and 18, can cause cervical cancer. These strains often do not cause symptoms until they have progressed to cancer.
Anal Cancer: High-risk HPV strains can also lead to anal cancer, which may cause symptoms such as anal bleeding, pain, itching, or changes in bowel habits.
Vaginal and Vulvar Cancer: High-risk HPV strains can cause vaginal and vulvar cancer, which may manifest as changes in the skin, chronic pain, itching, or the presence of a lump.
Penile Cancer: High-risk HPV strains can cause penile cancer, which may present as changes in the skin colour or thickness or the appearance of a painful sore.
Throat Cancer: High-risk HPV strains can cause throat cancer, which may include symptoms such as a sore throat, ear pain, constant coughing, pain or trouble swallowing or breathing, weight loss, or a lump or mass in the neck.
An individual’s immune status and physiological condition can influence the presentation and severity of HPV symptoms.
Immunocompromised Individuals
People with HIV/AIDS or individuals undergoing immunosuppressive treatments may find that their symptoms are more severe and persistent. These individuals are at a heightened risk of recurrent warts and potentially more rapid progression to cancers, as their immune systems are weak. Close medical follow-up and management are essential for them. They are also at a much higher risk of contracting HPV.
Pregnant Women
HPV symptoms in pregnant women can undergo changes. Hormonal fluctuations can cause genital warts to grow larger or multiply. In some cases, they might even bleed. While HPV does not typically affect the baby, there is a small risk of transmission during childbirth, which can affect the newborn. Hence, monitoring and appropriate management by healthcare providers are crucial.
If you notice any of these symptoms
Early Signs of HPV

Understanding the early indicators and symptoms of HPV is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Here are some of the initial signs and symptoms to watch for:
Initial Wart Appearance: One of the earliest signs of HPV is the appearance of warts. These can be small, raised, flesh-coloured bumps in the genital area, on the hands, or on the feet. They may appear singly or in clusters.
Changes in Skin Texture: Some individuals may notice changes in the texture of their skin where the virus has infected. This could manifest as rough patches or slight elevations that were not present before.
Mild Discomfort or Itching: Early HPV symptoms can include mild discomfort, itching, or irritation in the affected areas. This is not always intense but can be persistent, prompting further examination.
The timeline of symptom progression can vary widely. In most cases, the body’s immune system is able to clear the HPV infection before any visible symptoms appear. However, for those who do develop symptoms, genital warts can appear from several weeks to years after the initial infection.
HPV-related cancers may take a few years to develop after the initial infection.
Diagnosing HPV Symptoms
There are several methods used to diagnose human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, each with its own advantages and limitations. The key diagnostic methods include:
Medical Examination
The primary method for diagnosing genital warts is through a clinic diagnosis with a medical examination done by an experienced doctor. This involves a visual inspection of the cervix, vulva, vagina, and anus for any abnormal growths or lesions that may be indicative of HPV infection.
Pap Smear (Cytology)

A Pap smear is the collection of cells from the cervix, which is examined to see if there are abnormal cells. It is a widely used screening method that can detect precancerous changes. An Anal pap test may also be recommended for individuals who have exposure to anal sex.
HPV DNA Test
This test detects the presence of HPV DNA, which indicates an active infection. It is more sensitive than cytology for detecting precancerous changes and has higher reproducibility, as it is an objective, automated test. HPV DNA test is a recommended screening test for cervical cancer for women above 30 years old.
Stages of HPV Symptoms
The stages of HPV symptom development can be categorized into three main phases: initial infection, progression of symptoms, and long-term effects.
Initial Infection – HPV is typically transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, primarily during sexual intercourse or other intimate activities.
Progression of Symptoms – After initial infection, the virus may lie dormant for a period of time before symptoms start to develop. During this stage, the infected individual may not experience any noticeable symptoms or effects. However, some may experience genital warts.
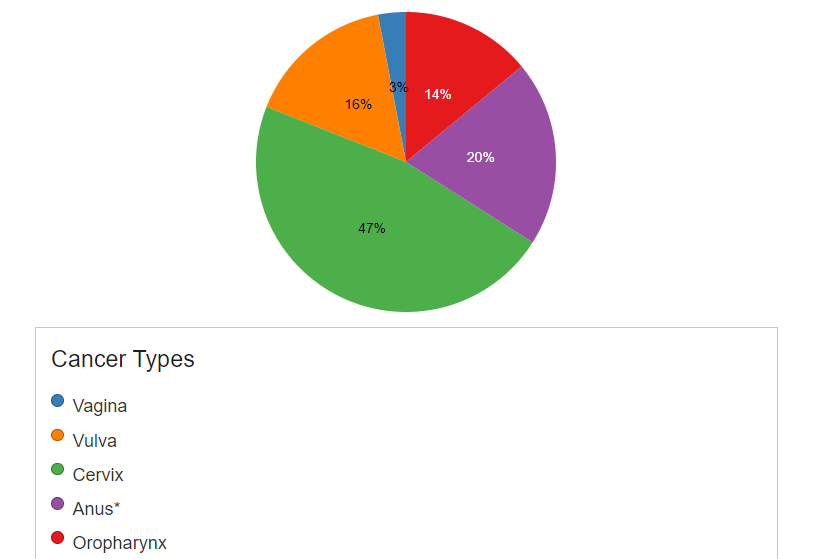
Long-Term Effects – If left untreated, high-risk type of HPV infections can lead to various types of cancer. In women, here are the cancer types that they may experience:
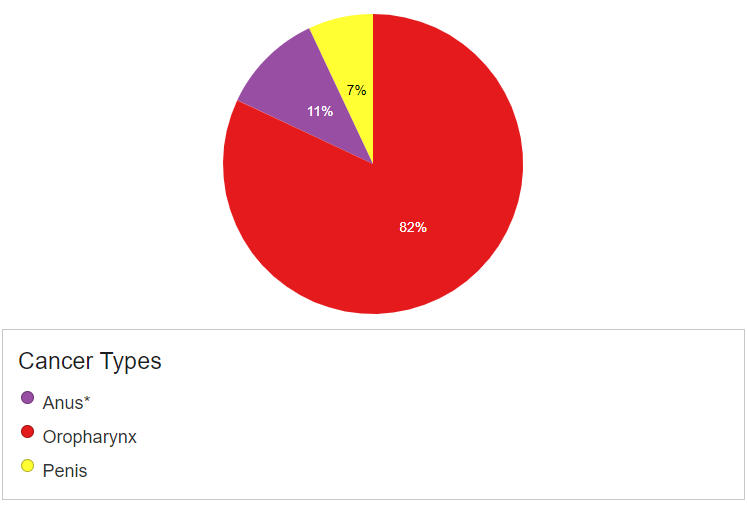
For men, here are the common HPV-related cancers that they may experience.
Can HPV Symptoms Be Treated?
Most HPV infections clear up on their own within two years without causing any problems. However, if it persists, treatments are available to manage symptoms like genital warts and precancerous cell changes.
If genital warts develop, they can be treated with prescription medications, freezing with liquid nitrogen to remove warts, or removed by burning with an electrical current. However, getting rid of the physical warts does not treat the underlying virus, and the warts may return.
For precancerous cell changes in the cervix caused by HPV, treatments like cryotherapy (freezing), conization (removing abnormal areas), laser therapy, or loop electrosurgical excision procedure can be used to remove the abnormal cells. The goal is to remove most or all of the cells with HPV before they progress to cancer.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you seem to have an HPV infection or experience concerning symptoms:
Genital Warts
Abnormal Bleeding
Abnormal bumps or growths over the genital region
For women, regular Pap tests can help any precancerous changes in the cervix early on.
Conclusion
Most HPV infections do not show any symptoms and typically resolve on their own without causing any significant health issues. The body’s immune system is remarkably adept at clearing the virus over time. However, for those with persistent infections or symptoms like genital warts, seeking medical advice is crucial.
Early detection and treatment help manage symptoms effectively and reduce the risk of complications. Regular Pap smear screenings for women are essential in catching any precancerous changes early.
If you notice unusual symptoms or have concerns, consult a healthcare provider for professional guidance and peace of mind.