Let’s face it: as women, we have a lot of responsibilities and decisions to make in our daily lives. And when it comes to pregnancy prevention methods, the choices can be overwhelming. Whether you’re just starting your journey or considering to switch to another method of birth control, it’s important to educate yourself on the various types of birth control available.
After all, choosing the right contraceptive can greatly impact not only your reproductive health but also your overall well-being. This guide will break down 11 different types of birth control methods, their benefits and side effects.
Say goodbye to confusion when it comes to taking charge of your own bodies to prevent unplanned pregnancies.
Hormonal Birth Control Methods
Hormonal birth control works primarily by altering hormone levels in the body to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the uterine lining. Below, we will discuss three common hormonal birth control methods: birth control pills, birth control patches, and birth control injections.
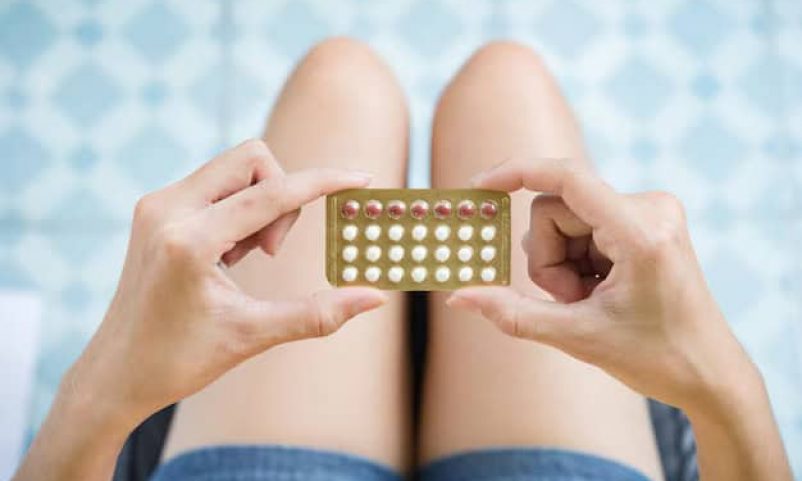
1. Birth Control Pills

Birth control pills, or oral contraceptives, involve taking a pill every day that contains estrogen and progestin, or progestin alone. These combination birth control pills prevent ovulation and thus prevent pregnancy. There are different types of pills, including combined oral contraceptive pills or progestin-only pills, each varying in hormone levels.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Birth control pills have an effectiveness rate of at least 93%. They can also offer benefits such as regulated menstrual cycles, reduced acne, and relief from menstrual cramps.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Some common side effects of a birth control pill may include nausea, weight gain, mood changes, and breast tenderness. It is important to consider that the pill does not prevent sexually transmitted infections and must be taken consistently every day to maintain effectiveness.
The pill also requires a doctor’s prescription in Singapore.
2. Birth Control Patch
A birth control patch is an adhesive patch placed on the skin that releases hormones (estrogen and progestin) into the bloodstream. The patch needs to be replaced weekly for three weeks and a patch-free week to allow for menstruation.
Benefits and Effectiveness
When used correctly, the birth control patch is at least 92% effective. It offers a convenient, once-weekly application and helps regulate menstrual cycles.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Users might experience skin irritation at the application site, as well as other side effects similar to those of birth control pills, such as nausea and breast tenderness. As with pills, the patch does not protect against STIs.
3. Birth Control Injection
The birth control injection, or contraceptive injection, commonly known as Depo-Provera, involves receiving a hormone injection (progestin) from a healthcare provider once every three months. This method works by preventing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus.
Benefits and Effectiveness
The contraceptive injection is highly effective, with a typical use effectiveness rate of at least 95%. It provides long-lasting protection and may reduce the frequency and severity of menstrual cramps.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Some users may experience irregular menstrual bleeding, weight gain, and decreased bone density with long-term use. The injection does not protect against STIs, and it may take some time to regain fertility after discontinuation.
Barrier Methods
Barrier methods are generally easy to use and do not involve hormones, making them a popular choice for many individuals. These methods of birth control work to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Two common barrier methods are condoms and diaphragms.
4. Condoms

There are male (worn over the penis) and female (inserted into the vagina) condoms. Both types are usually made from latex or polyurethane.
Usage Instructions
To use a male condom, place it on the tip of the erected penis and unroll it down to the base. Ensure there are no air pockets and that the condom fits snugly. For female condoms, insert the closed end into the vagina, and ensure the outer ring covers the external genitalia.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Condoms are effective when used correctly and being a barrier method, it also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Some may have allergic reactions to latex. Improper use can also lead to reduced effectiveness. A condom can also break, tear or leak which makes it not effective at preventing pregnancy. In such situations, the girl may have to take the morning after pill as a form of emergency contraception.
As such, condoms are not recommended solely for the use of family planning and other methods that are more reliable are recommended.
Long-acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) represents a highly effective and convenient option for preventing pregnancy. These methods require minimal maintenance once in place and can last several years, offering significant benefits to individuals seeking long-term control over women’s health.
5. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
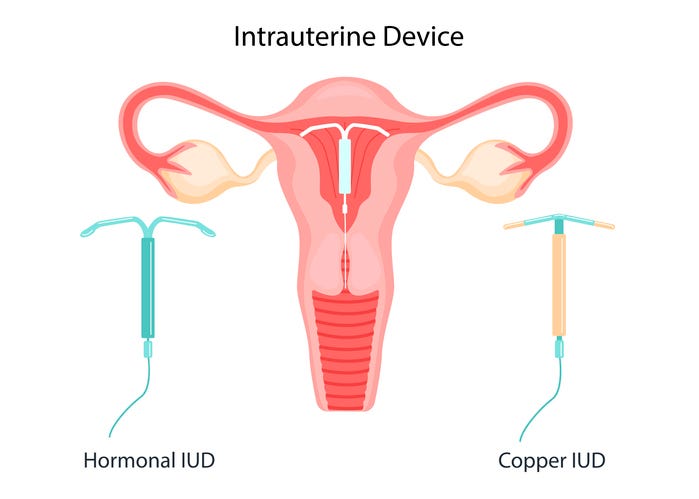
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. There are two types of IUDs: a copper IUD and a hormonal IUD.
Types: Copper vs. Hormonal
Copper IUDs do not contain hormones. Instead, the copper acts as a spermicide, preventing sperm from fertilising an egg. It can be effective for up to 5 years.
Hormonal IUDs release tiny amounts of progestin, which thickens cervical mucus and suppresses ovulation. The hormonal IUD can last up to 5 years as well. The main hormonal IUD used in Singapore is called the Mirena.
Insertion Process
The insertion of an IUD is a quick procedure that is performed in a healthcare provider’s office. During the insertion, the provider will insert a speculum into the vagina, similar to a pelvic exam, then place the IUD through the cervical canal into the uterus. Some discomfort or cramping may be experienced during and immediately following the insertion.
Benefits and Effectiveness
IUDs are included among the most effective birth control, with an effectiveness rate of over 99%. They provide long-term protection and require minimal maintenance after insertion. Hormonal IUDs may also reduce menstrual bleeding and cramping.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
IUDs may cause irregular bleeding, especially within the first few months of insertion. Some users of hormonal IUDs experience hormonal side effects such as irregular spotting, menstrual changes or having their periods stop completely, while Copper IUD users may increase menstrual bleeding and cramping, particularly in the first few cycles.
Additionally, there is a small risk of the IUD perforating the uterus or becoming displaced. Importantly, IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are advised to ensure the IUD remains correctly positioned and for any concern that may arise.
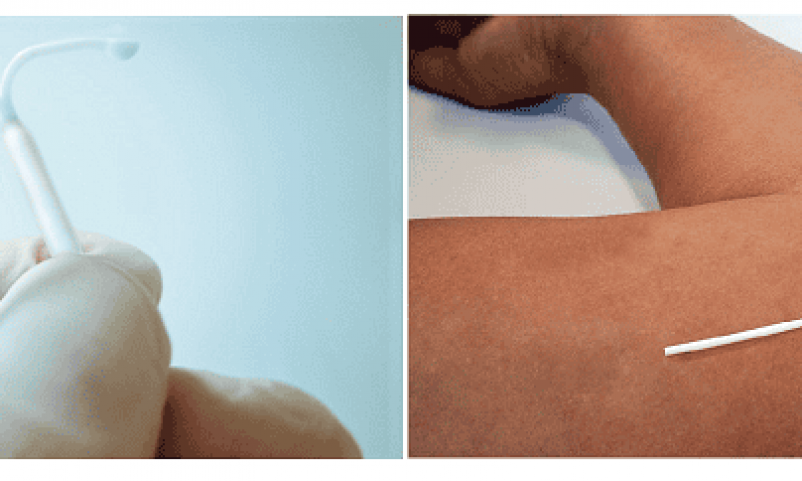
6. Contraceptive Implants

Contraceptive implants are another form of LARC involving a flexible plastic rod that is inserted under the upper arm’s skin. The insertion process is quick, typically completed in a healthcare provider’s office under local anaesthesia. The implant releases progestin steadily, which prevents ovulation, thickens mucus in the cervix, and thins the uterine lining to prevent pregnancy.
Benefits and Effectiveness
This method is noted for its high effectiveness, with a failure rate of less than 1%. One of the main benefits is that it can last for up to 3 years, providing long-term contraception without the need for daily pills or frequent doctor visits.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Possible side effects of contraceptive implants include irregular periods or spotting. Some users may also experience headaches, breast tenderness, mood changes and weight gain.
Permanent Methods
The permanent method is chosen by individuals who no longer want any or more children. This section covers two primary permanent methods: tubal ligation and vasectomy.
7. Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation involves cutting, tying, or sealing the fallopian tubes so that eggs don’t reach the uterus. This is done via a surgical procedure. The recovery process typically involves a few days of rest and some mild discomfort.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Tubal ligation has a high effectiveness rate, often quoted as over 99% and the peace of mind it provides to those certain they do not want future pregnancies. It is a one-time procedure that doesn’t require ongoing maintenance or repeated visits to healthcare providers, making it a convenient option for many.
Considerations and Permanence
Considerations must include the permanence of this decision, potential surgical risks, and the fact that reversal procedures, although possible, are not guaranteed to restore fertility. While highly effective in preventing pregnancy, tubal ligation does not offer protection against STIs.
8. Vasectomy
A vasectomy is a minor surgery for men, where tubes that carry sperm from the testicles (vas deferens) are cut and sealed. The procedure is usually quick and often completed within 30 minutes under local anaesthesia. The recovery process is generally short, with many men returning to normal activities within a week, although it is advised to avoid strenuous activities for a few days.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Vasectomies are highly effective, with less than a 1% chance of pregnancy post-procedure. It is a one-time procedure and eliminates the need for other forms of contraception.
Considerations and Permanence
It is important to be absolutely certain about not wanting more children before undergoing a vasectomy, as the procedure is considered permanent. While reversals are possible, they are expensive and not always successful. Men should also consider that vasectomies do not provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Birth Control Method
When selecting among birth control options, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure the choice aligns with personal needs and preferences.
Personal Health and Medical History
Your health and medical history are crucial in determining the most appropriate birth control method. Certain conditions like high blood pressure, migraines, or a history of blood clots may make some options less suitable.
Lifestyle and Convenience
The ease of use and how a birth control method fits into your daily routine is another important consideration. Methods like daily pills require consistent habits, while options such as intrauterine devices (IUDs) or implants offer long-term protection with minimal maintenance.
Cost and Accessibility
The affordability and accessibility of different birth control methods can vary significantly. Some methods may be expensive without insurance coverage, while others might be available at low or no cost through healthcare programmes and clinics.
Partner’s Involvement and Preferences
Open communication with your partner about birth control preferences and involvement is important. Shared responsibility and mutual comfort with the chosen method can enhance its effectiveness and reduce potential conflicts.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Use
Consider whether you need a long-term or short-term birth control solution. While condoms or pills are suitable for temporary use, options like IUDs or implants provide long-term solutions without the need for frequent attention.
Ethical and Religious Considerations
Personal beliefs can significantly influence birth control choices. Some individuals or couples may prefer methods that align with their ethical or religious values, and it is important to respect and incorporate these beliefs into the decision-making process.
Conclusion
There are various birth control methods, each with its unique benefits, considerations, and effectiveness. Understanding the available options empowers individuals to make informed choices.
Women should also consider personal health, lifestyle convenience, cost, partner involvement, duration of use, and timeline for starting a family when selecting a birth control method.
It is highly encouraged to consult with healthcare providers who can offer personalised advice and help navigate the complexities of each option. They can provide relevant medical insights, assess any potential risks, and suggest methods that fit your lifestyle and health profile.
Taking the time to evaluate and discuss your preferences ensures that you select the most appropriate and effective birth control method for your situation.