Vaginal lumps, bumps and blisters are one of the most common symptoms that women present with at a women’s health clinic.
These symptoms are common, yet are a source of great distress for many women.
They may sometimes be associated with other symptoms such as pain or itch, and is usually either noticed incidentally by the patient or by their partners.
Vaginal lumps, bumps and blisters can be due to a variety of causes, ranging from benign lumps to sexually transmitted diseases.
Here are 9 most common causes of vaginal lumps, bumps and blisters to look out for!
1. Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is one of the most commonly seen causes of vaginal bumps and blisters in women. It is a type of sexually transmitted disease caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus.
Genital herpes usually causes painful blisters around the labia region (skin folds around the vagina).
Patients usually experience tingling, pain or soreness around their genital region with blisters or ulcers seen.
The herpes virus is usually spread via sexual contact, with the fluids being very contagious when the active blisters are present.
There are 2 main strains of the herpes virus that most people have heard of, namely HSV Type 1 and HSV Type 2.
While the HSV Type 1 virus is usually more associated with oral blisters or cold sores, this can easily be transmitted to the genital area, especially through oral sex.
Treatment: The herpes virus can be tested via a swab test called a PCR test. Treatment for herpes is usually with antiviral medications.
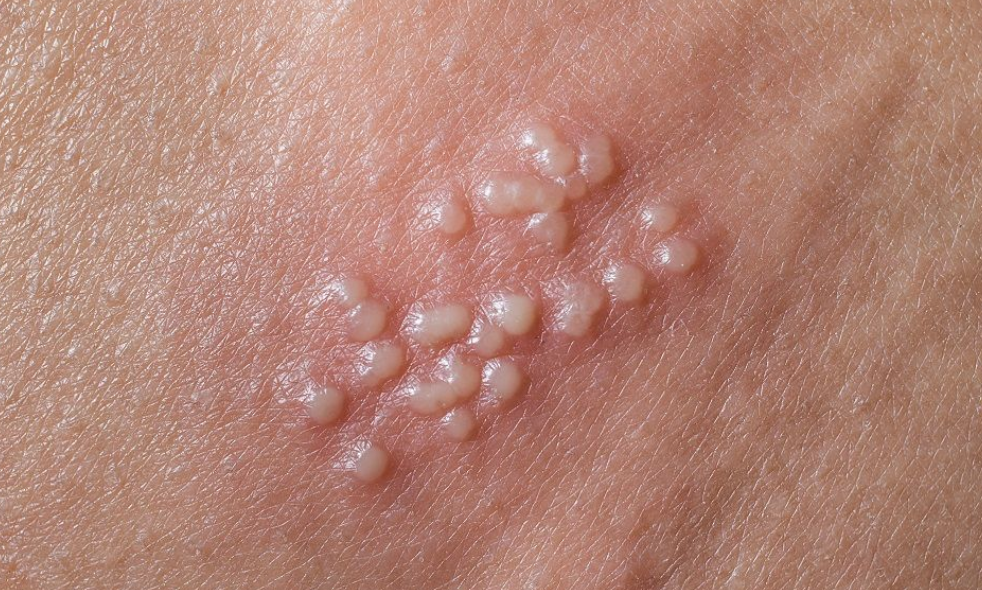
2. Genital Warts
Genital warts are also a type of sexually transmitted disease.
They are caused by the Human Papilloma Virus. Warts are usually painless, and may appear as multiple small skin coloured or cauliflower like bumps over the genital area.
These bumps can appear as individual growths, or more commonly in multiple lesions. Genital warts are also spread via sexual contact and are very contagious.
Treatment: Genital warts can be treated in various ways, ranging from topical medications such as Imiquimod or Podophyllin Toxin, Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen freezing), Electrocautery or Laser removal.
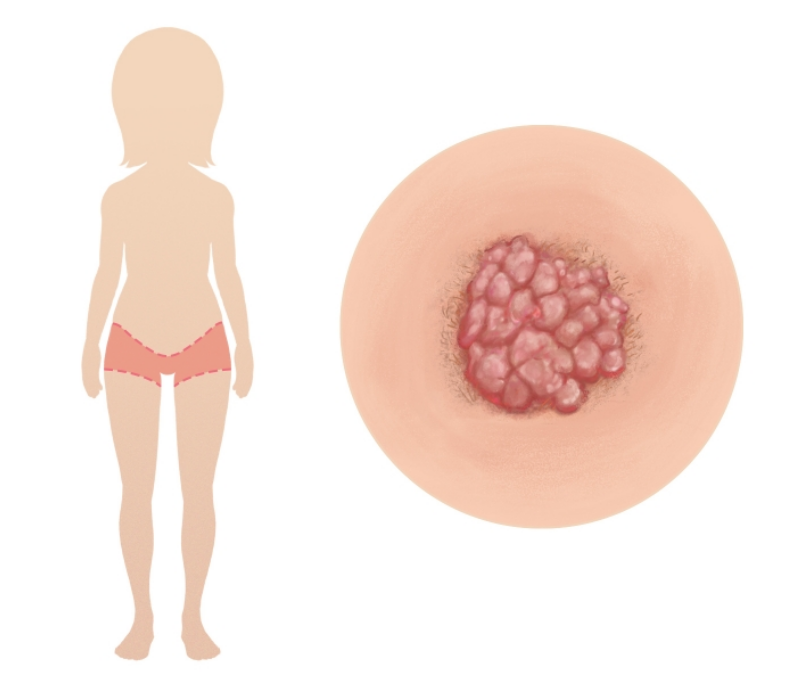
3. Abscess
Abscesses around the genital region are relatively common due to the presence of bacteria around the skin and hair there.
Just like how we get pimples or acne due to clogged pores and bacteria on our face, abscesses can form around our genital regions due to bacterial infection of the skin around there.
Treatment: Abscesses can be treated with oral or topical antibiotics. Sometimes the doctor may perform a drainage of the abscess to help it heal faster.
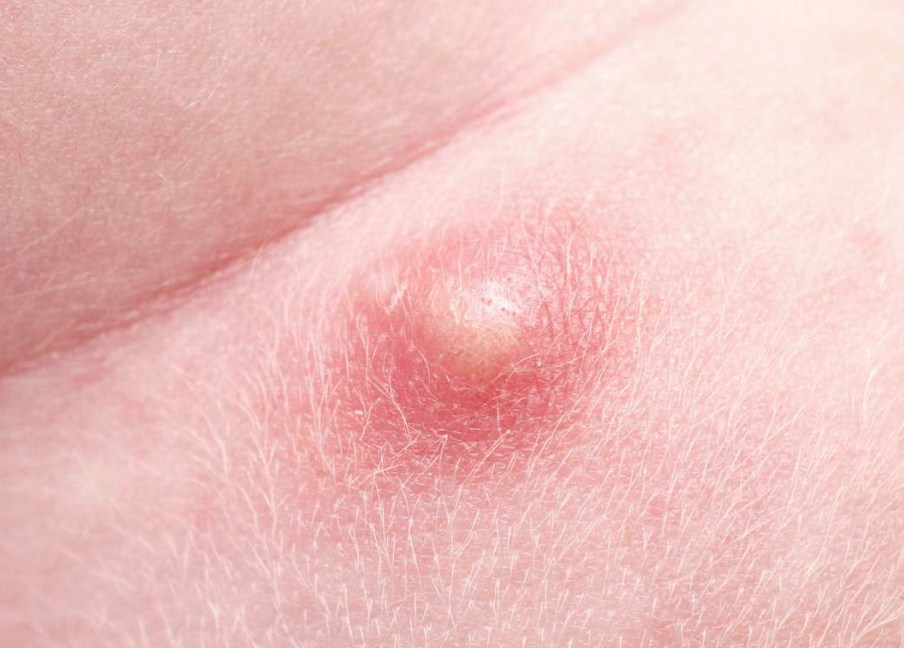
4. Molluscum Contagiosum
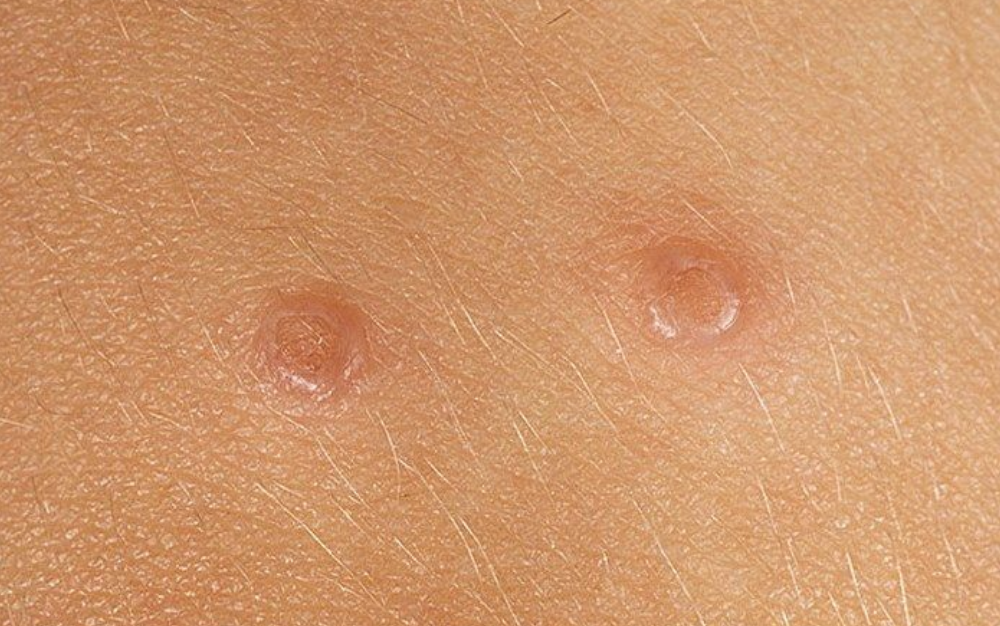
Molluscum is a type of skin infection caused by the virus Molluscum Contagiosum. These skin lesions usually appear as flesh-coloured bumps around 1-2cm in size and are painless and not itchy.
The virus is usually spread through direct contact such as skin-to-skin contact or through contaminated towels or clothes.
Molluscum can resolve on its own over a few months, but treatment can be done to get rid of it in a much faster time.
Treatment: Topical medications such as Imiquimod or Podophyllin Toxin, Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen freezing), Electrocautery or Laser removal.
5. Vestibular Papillomatosis
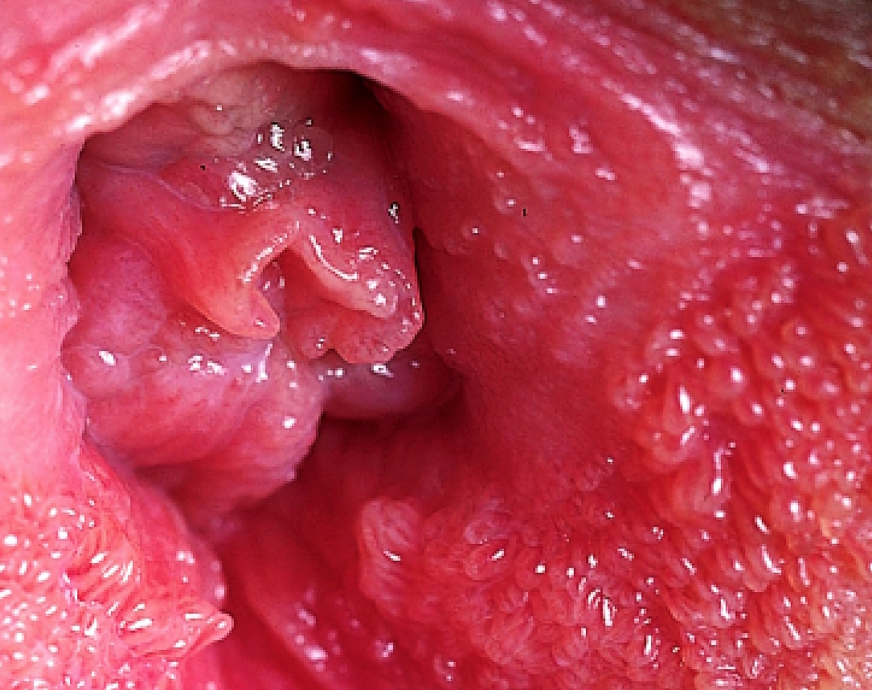
Vestibular Papillomatosis refers to tiny bumps or finger-like projections that are found over the labia minora or vaginal opening.
As scary as its name sounds, this is actually just a part of your normal vaginal tissue!
These tiny bumps around the vaginal area are very commonly mistaken for genital warts, which have caused a lot of unnecessary worry in patients or have led to unnecessary treatments being carried out.
Treatment: No treatment is required for this, as this condition is harmless and just a part of your normal vaginal tissue.
6. Folliculitis
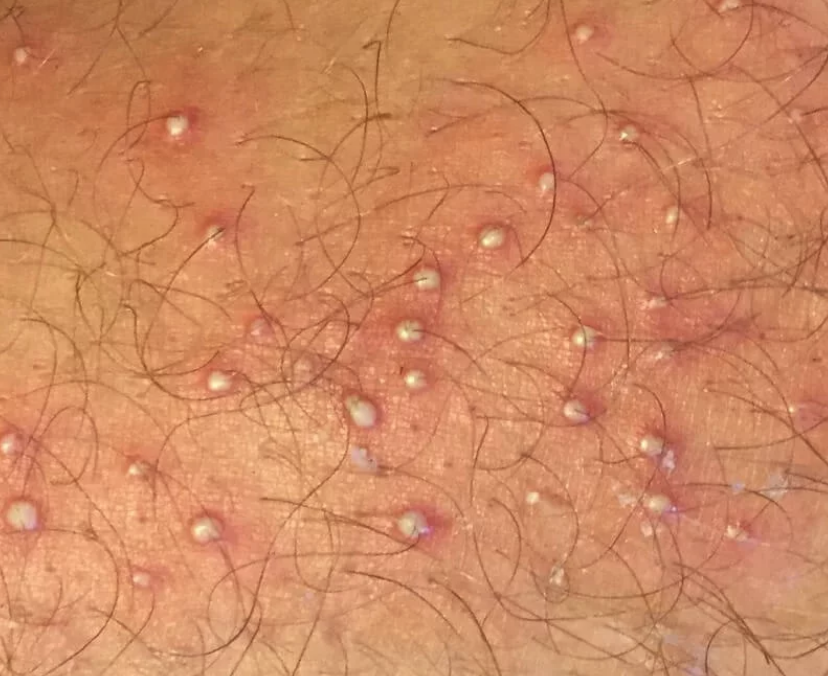
Hair follicles or ingrown hair around the pubic or labia region can get infected leading to painful tiny bumps around the area.
This is usually caused by minor infection of the hair follicles there.
This is a relatively common problem, especially in women who shave.
Treatment: Topical antibiotics can be applied to reduce the inflammation of the hair follicle. Practising good hygiene can also reduce the risk of infection.
7. Bartholin’s Cyst/Abscess
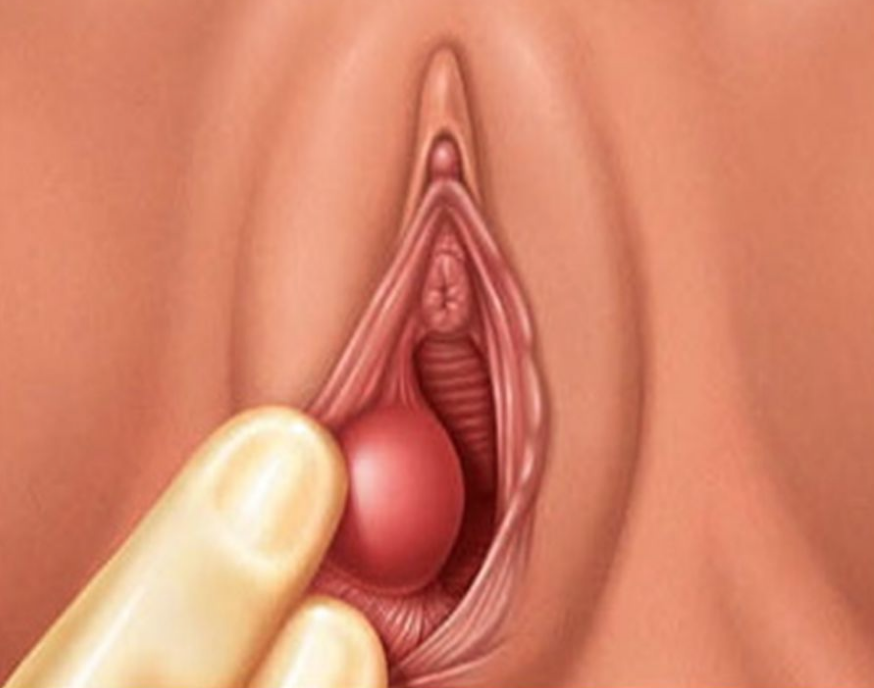
The Bartholin Gland is a tiny gland that is located at each side of the opening of the vagina.
The Bartholin Gland’s purpose is to secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina, especially during sexual arousal.
This gland commonly gets blocked which leads to the formation of a cyst known as Bartholin’s Cyst.
Sometimes this cyst can get infected with bacteria forming an abscess, which is then referred to as a Bartholin’s Abscess.
The cyst may or may not be associated with some pain. However, once an abscess is formed, pain and discomfort are commonly experienced with many women having trouble sitting down or walking due to the pain.
Treatment: Cysts or Abscesses can usually be treated with antibiotics. However, if the size of the cyst or abscess is too large, a simple procedure called an incision and drainage may be performed. An additional procedure called Marsupializaton may also be done to prevent this cyst from recurring.
8. Sebaceous Glands
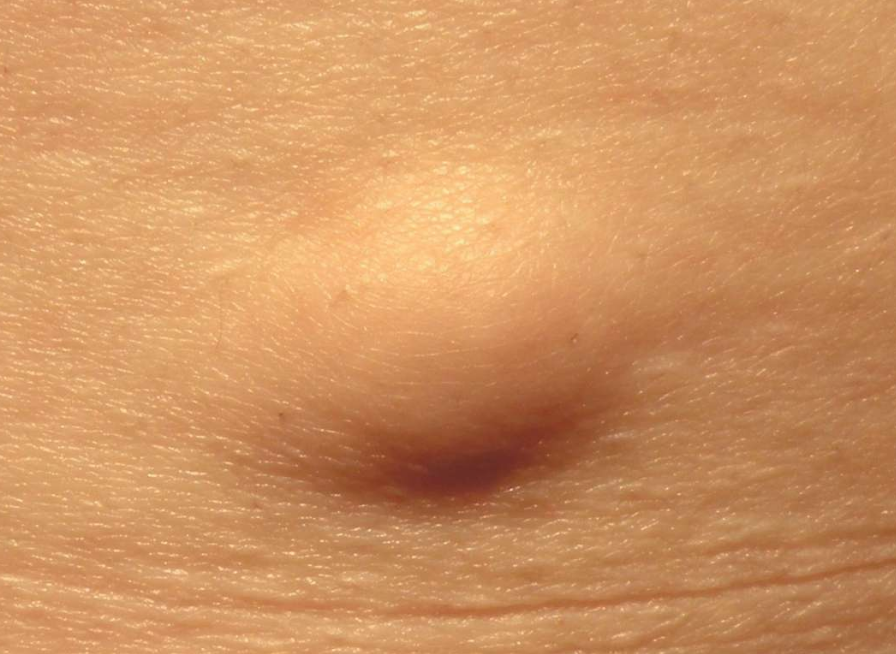
Our skin contains oil glands known as sebaceous glands. This applies to the skin around our whole body, including the skin around our private areas.
When these oil glands get blocked, they may form tiny bumps or lumps on the skin which are known as sebaceous cysts. These are usually painless but may grow in size over time.
Treatment: These sebaceous cysts or glands are usually harmless, but may carry a small risk of getting infected. Some people may find them unsightly or uncomfortable. These may be removed via a minor surgery if required.
9. Cancer

Last but not least, abnormal lumps and bumps around the vulva or vaginal area can also be attributed to cancer.
Vulva and vaginal cancer however, is rare overall and usually affect women in the older age group. Some of these cancers in the vulva or vaginal region are known to be caused by the Human Papilloma Virus.
The good news is that we now have the HPV vaccination to protect and reduce our risk of potentially getting affected by this.
Treatment: If a suspicious lump is seen by the doctor, a biopsy may be taken. If the diagnosis of cancer is confirmed, you will usually be referred to the oncologist and may require surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy.