You’ve just finished having sex with your partner, you look down and you notice some blood. But you’re not supposed to be having your period just yet. Is bleeding after sex supposed to happen?
Alarm bells start ringing and your mood for any further intimate moments of passion is lost immediately.
Is this supposed to be normal?
Well, the answer is both yes, and no.
What Causes Bleeding After Sex?

Bleeding after sex is known in medical terms as postcoital bleeding.
The only time some bleeding may be expected is, as we all know, when a girl first loses her virginity. This bleeding comes from the breaking of the hymen.
Is Bleeding After Sex Normal Even If It’s Not Your First Time?

Post-coital bleeding is not as uncommon as we think it is.
There can be a whole spectrum of various causes of post-coital bleeding, ranging from benign causes to more sinister ones including cervical cancer.
Here is what’s important – do get yourself checked by an experienced women’s health doctor should you experience such symptoms.
What Are The Common Causes Of Post-Coital Bleeding?

The bleeding can arise from local causes from the vagina, cervix or more rarely, the womb. Majority of the patient’s I see have nothing major to worry about, but that is only after all relevant investigations have been dutifully carried out!
Therefore, it is important for you to arrange for a consultation with your doctor if you have experienced any of such symptoms, so that we may ascertain the cause of the bleeding and start appropriate treatment in a timely manner.
Here’s a low down on the common reasons why you could be experiencing bleeding after sex, and what to do about it:
1. Yeast Or Bacterial Infection

Yeast infection, also known as candida, or bacterial infection, commonly known as Bacterial Vaginosis, are 2 prevalent causes of vaginal infections in ladies.
Vaginal infections can cause inflammation of the cervix or vagina, which can lead to bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Fret not; these infections are NOT sexually transmitted diseases.
Instead, how they commonly arise is due to the imbalance of vaginal bacteria levels, which can lead to their overgrowth. This imbalance is commonly triggered by factors such as changes in vulva hygiene or habits, stress or frequent sweating.
What To Do: The good news is that these very common vaginal infections are easily treatable with appropriate medications given by an experienced doctor. You will also be advised on proper vulva hygiene to prevent recurrences. Treatment of these infections can usually resolve your symptoms.
2. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)

Chlamydia and Gonorrhea are 2 common examples of sexually transmitted diseases in women.
For women who are sexually active, especially those who have unprotected sex with multiple partners, you are more prone to getting a sexually transmitted disease.
Majority of the time, infected women may not have any active symptoms, and post coital bleeding may be the only indicator of an STD. This is again due to the inflammation of the cervix or vaginal tissues, which causes it to become more friable and hence bleed easily.
What To Do: It is crucial to diagnose and treat STDs early in women, especially those in their 20s or 30s, as untreated STD infections can lead to infertility in the long run.
3. Cervical Or Endocervical Polyps
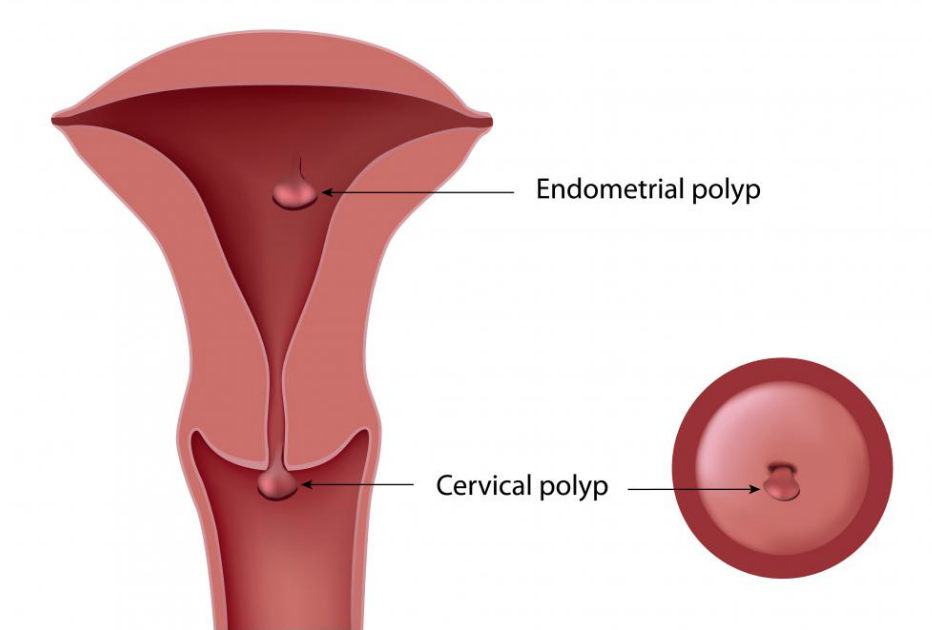
Polyps are relatively common. They are little growths that can arise from the cervix, endocervical canal or womb. They are usually 1-2cm in size. While the idea of having polyps may sound intimidating, the good news is that these polyps are usually benign most of the time. These polyps are common, especially in premenopausal women who have a higher amount of female hormones in their body.
Polyps are made up of soft tissue, causing them to bleed easily. This happens especially with direct contact, which occurs during sex. Sometimes, they may even cause bleeding at random, which causes a patient to experience abnormal spotting out of her menstrual cycle.
What To Do: Cervical polyps are usually detected when your doctor examines your cervix. If seen, they can be easily removed. Removal of the polyp will allow us to send it for a biopsy to ensure the cells are benign.
4. Cervical Ectropion
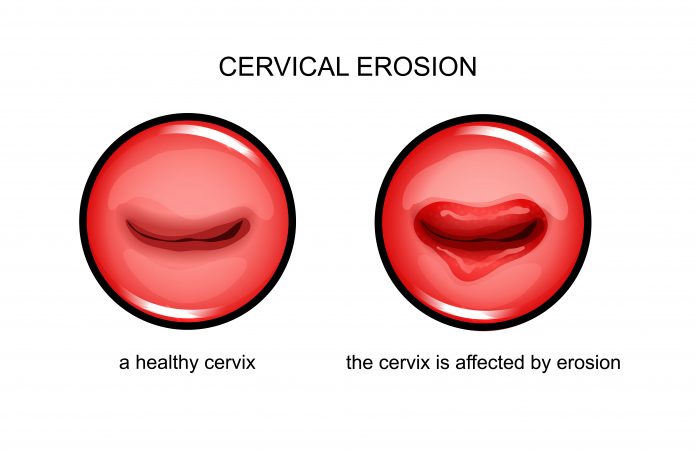
Cervical ectropion is more simply known as superficial inflammation or erosion of the cervix. This is not a dangerous condition and in fact is extremely common in normal women.
Ectropion occurs when the ‘inner’ glandular cells appear on the outer area of the cervix, giving it a reddish appearance. This area contains blood vessels, which can lead to bleeding when ‘traumatized’ after sex.
What To Do: Cervical ectropion can usually be observed, however, some medication may be prescribed if your symptoms are persistent. It is also important to ensure you have an up-to-date PAP smear.
5. Pregnancy
Postcoital bleeding may be an early sign of pregnancy due to the increased blood vessels around the cervix. On top of this, if you are already pregnant and experience bleeding after sex, you should get it checked by your doctor to ensure that the bleeding is not due to a miscarriage.
What To Do: Pregnancy should always be ruled out, especially in young sexually active females. If you are already pregnant and experience bleeding, do consult your doctor early to rule out any serious causes.
6. Rough Sex

Over enthusiastic moments of passion can cause micro tears in the blood vessel-rich tissues of the cervix or vagina, which can lead to bleeding after sex. Other contributing factors can include having sex in different positions or the use of sex toys.
What To Do: Go easy on yourself! Should you experience a large amount of bleeding, seek a doctor’s opinion immediately as larger tears may require surgical repair.
7. Vaginal Dryness

Vaginal dryness, also known as vaginal atrophy, can also lead to post coital bleeding. Older women who are undergoing menopause or who are already menopausal usually experience this. The vagina maintains natural lubrication via the female hormone estrogen.
During menopause, the levels of estrogen in females fall to a low level. This in turn results in dryness in the vaginal area.
Vaginal atrophy can lead to painful sex, or bleeding after sex.
What to do: Use lots of lubricant so that you may have an easier time. If the bleeding is persistent, it is important to get it checked by an experienced women’s health doctor to exclude a more sinister cause.
8. Cervical Cancer
The nasty C word we all don’t want to hear about. Unfortunately, post-coital bleeding can also be one of the symptoms of cervical cancer.
This is because any tumour or growth around the cervix is usually friable which can also lead to abnormal bleeding when coming into contact during sex.
The good news, however, is that cervical cancer is preventable and detectable.
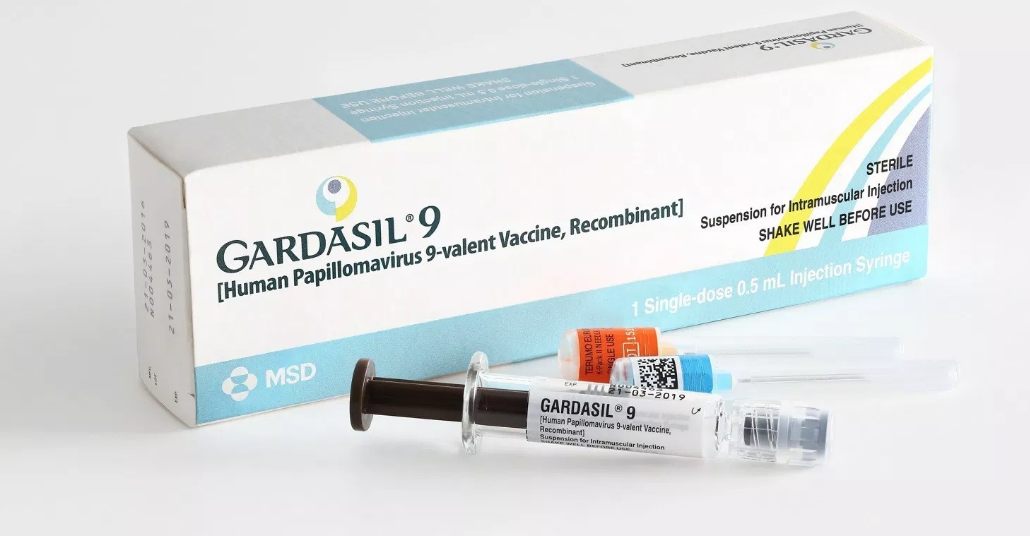
The latest Gardasil 9 vaccine is available to protect us from the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), which is the virus known to cause cervical cancer. Regular PAP smears with HPV co-testing also allows us to pick up abnormal cells at a much earlier stage and treat it before it turns into cancer.
What To Do: Make sure you’re vaccinated against HPV, and have your regular PAP smears done!
In Conclusion
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, do make an appointment with your women’s health specialist to get yourself checked!