If there was a way to detect abnormal pre-cancer cells through a very simple test, before invasive cancer develops – will you do it?
Definitely yes!
Well this test exists – and it is called a PAP smear.
What Is A PAP Smear?

Surprisingly, many women have actually not heard of a PAP smear before.
This is despite the increased efforts to raise awareness in recent years with free PAP smear screening by the government.
A PAP smear is basically a simple test performed which screens cells from your cervix, or the neck of the womb, to look for cervical cancer or pre-cancer cells. This helps to detect cervical cancer even in the early stages.
Doing so allows cancer to be diagnosed at a much earlier stage, allowing for faster treatment intervention and significantly improving your chances of survival.
Tests these days also include co-testing with Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), which is the virus responsible for causing cervical cancer in women.
Why Is A PAP Smear So Important?
According to the WHO statistics, cervical cancer is the 4th most common cancer in women in the world. In Singapore, it ranks number 10 (according to statistics from Singapore Cancer Society).
This reduction in the prevalence of cervical cancer in Singapore can be attributed to the increase in PAP smear screening in women as well as the development of the HPV vaccine in recent years.
Cervical cancer can be:
- PREVENTED EASILY
- DETECTED EARLY
- TREATED EARLY
All these can be achieved through regular PAP smear screening as well as the HPV vaccine.
What Is The Human Papilloma Virus?
The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is essentially the virus that is the main culprit for cervical cancer, as well as other diseases such as:
- Genital Warts
- Vaginal Cancer
- Anal Cancer
- Penile Cancer and so forth
There are over 100 different strains of HPV, of which 15 of them are classified as highly likely to cause cancer. In most cases, cervical cancer is attributed to two types – HPV-16 and HPV-18 (high-risk HPV).
HPV can affect almost any woman who has ever had sexual intercourse before.
However, many women affected by HPV are actually able to clear the infection on their own within 2 years.
Those who have persistent infections will tend to be at an increased risk of developing cervical abnormalities and eventually cervical cancer.
Who Needs Regular PAP Smear Screening?
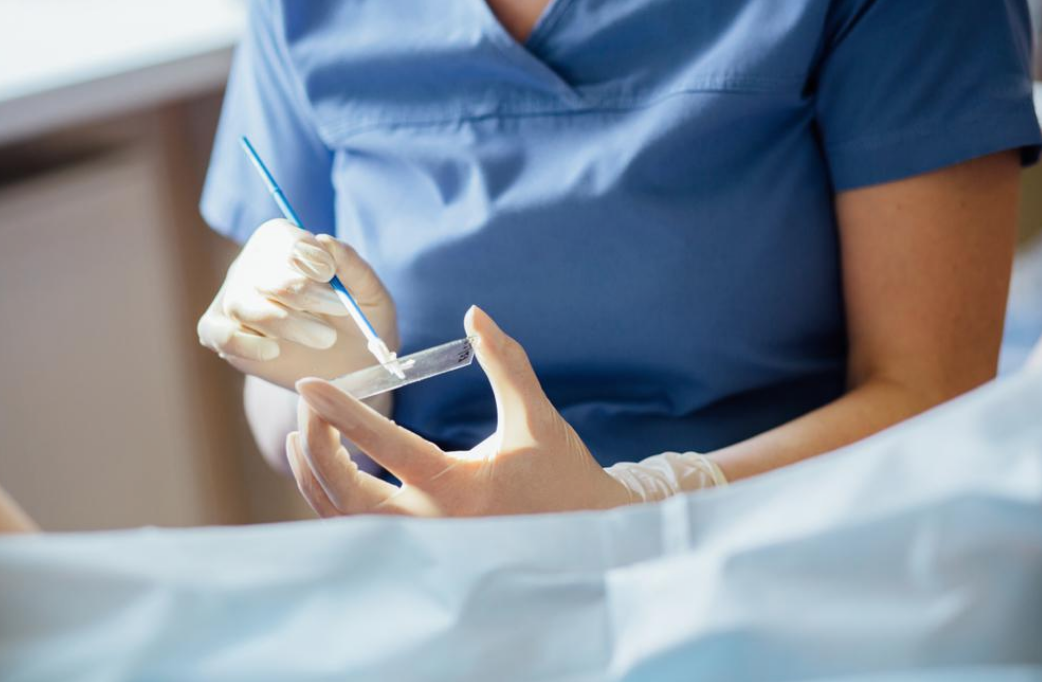
Any girl who has ever had sexual intercourse before will need to have regular PAP smear screening starting from the age of 21 to 65 years old.
This is because exposure to HPV occurs through sexual contact.
If you have NEVER been sexually active in your life, then you DO NOT need to do a PAP smear.
How Often Do I Need A PAP Smear?
PAP smear screening is usually recommended for girls from 21 years old and above.
The recommended screening is from 21 years old to 65 years old.
PAP Smear screening is done once every 3 years if your results are normal.
PAP Smear + HPV Co-testing can be done every 5 years.
(HPV Co-testing is only recommended for women 30 years old and above)
This recommended schedule only applies for women with normal results.
Women with an abnormal PAP smear will require more frequent testing.
How Is A PAP Smear Done?

It takes approximately 30 seconds to 1 minute to perform a PAP smear.
That is how easy it is!
You will be asked to lie on the examination couch with your knees bent up and legs apart.
A small plastic device called a speculum will be gently inserted into the vagina for the doctor to directly visualize the cervix. This may be slightly uncomfortable for you.
The PAP smear is then taken directly from the cervix with a special brush or broom and sent to the laboratory for testing.
A PAP smear may be uncomfortable, but should not be too painful for you, especially if you have it done with an experienced women’s health doctor.
What Is The Difference Between A Regular PAP Smear and HPV Testing?
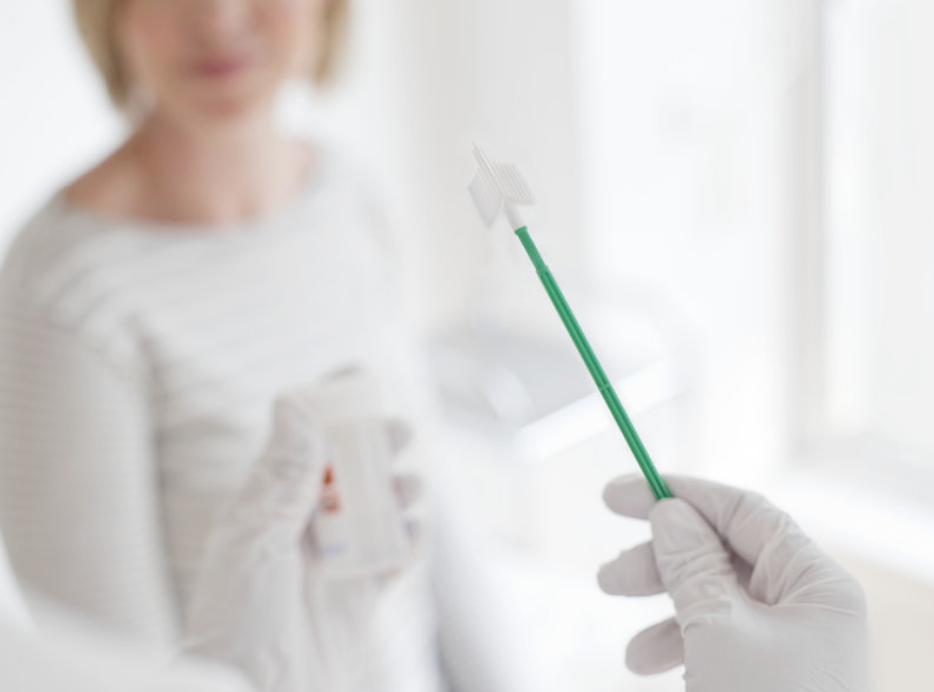
A regular PAP smear only detects the presence of abnormal cell changes in your cervix.
The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is the virus, which serves as the culprit behind cervical cancer or precancerous changes.
Hence, HPV testing serves as a more accurate form of testing which is able to pick up the presence of the virus even before it can cause any cell changes.
HPV testing also helps your doctor have a better idea on what the next best course of action will be.
If a high-risk strain of HPV is picked up, you may be required to go for further testing eg Colposcopy, or may be required to repeat your PAP and HPV test at a closer interval (eg 6 months to 1 year instead of 3 to 5 years).
How Is HPV Testing Done?
Testing for the HPV virus is done exactly the same way as how a PAP smear is done. Not to worry, the process is not more painful just because an HPV test is being added.
An HPV test can also be done at the same time as the PAP smear so that the doctor is able to collect samples to send for both types of testing.
What Happens If My Results Are Abnormal?
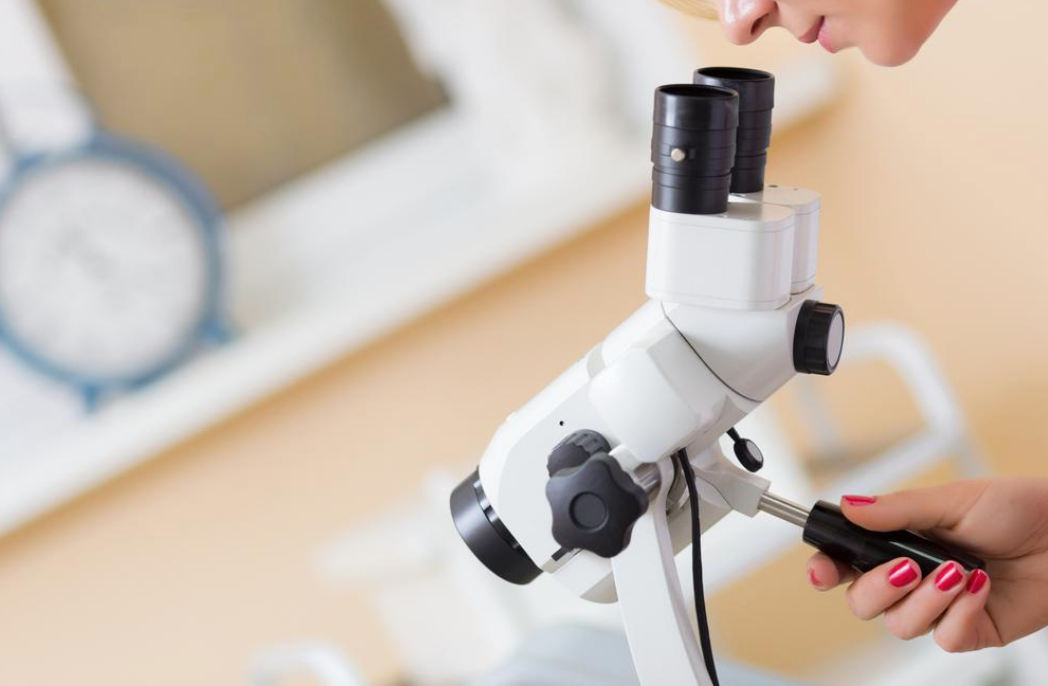

If your PAP smear results return with an abnormal result, you may be referred for a further procedure called a Colposcopy.
This will allow us to have a closer evaluation of the cervix and to assess the abnormalities present.