A PAP Smear is a simple yet important procedure that could be lifesaving.
This is a test that is done to screen for early cervical cancer.
This is crucial for women and is one of the best ways to detect early cervical cancer and prevent it from developing into invasive cancer.
Contents
- 1 PAP Smear Screening
- 1.1 What Is Cervical Cancer?
- 1.2 What Is A PAP Smear?
- 1.3 Why Do I Need A PAP Smear?
- 1.4 Who Is At Risk of Cervical Cancer?
- 1.5 How Often Should A PAP Smear Be Repeated?
- 1.6 How To Prepare for a PAP Smear?
- 1.7 How Is A PAP Smear Conducted?
- 1.8 What Happens After The PAP Smear?
- 1.9 What Happens If You Get An Abnormal PAP Smear Result?
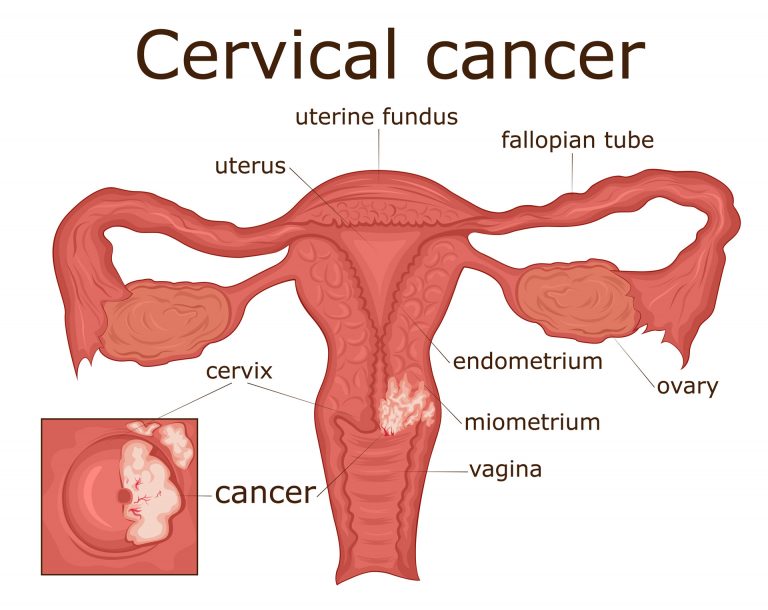
What Is Cervical Cancer?
The cervix is a part of the female reproductive system, also known as the neck of the womb.
Cervical Cancer is the 4th most common cancer in the world.
In Singapore,statistics from the Singapore Cancer Society show that it is the 10th most common cancer in women. The reduced prevalence in Singapore is attributed to increasing awareness in women for regular pap smear screening and also the HPV vaccine.
Cervical cancer is caused by infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). This leads to abnormal cell changes which eventually progress to cancer.
What Is A PAP Smear?
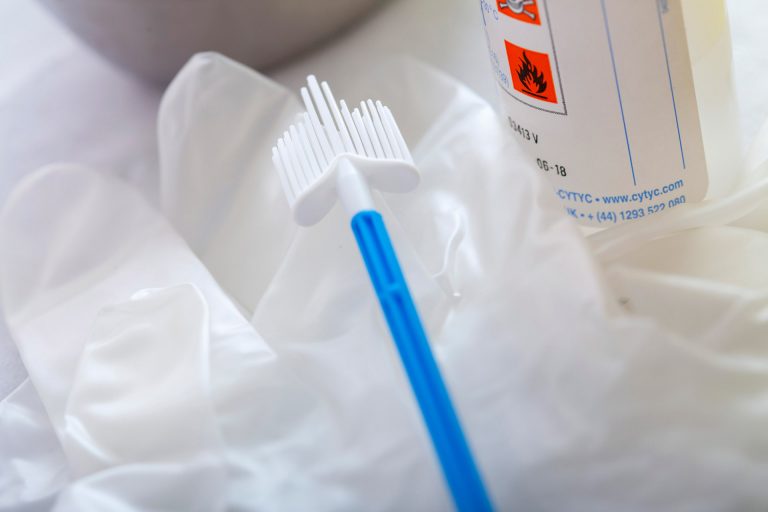
A PAP Smear is a test that involves obtaining and analyzing cells from the cervix.
This has been widely recognised as an effective way to detect early-stage cervical cancer.
It is affordable and easily accessible in most countries, and crucial in detecting and thus preventing early-stage cervical cancers from developing into a more invasive cancer.
A Pap Smear is used in cervical cancer screening to detect:
- Early cancerous cells
- Pre-cancerous cells
Other than that, a Pap smear may also detect:
- Infection
- Inflammation
- Certain sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, etc.)
Why Do I Need A PAP Smear?
It is crucial for women to screen for cervical cancer as it is extremely preventable and treatable if detected early.
The early stages of cervical cancer usually do not display any physical symptoms. Thus, it often goes undiagnosed and left untreated. Unfortunately for some women, the cancer is only detected after it reaches an invasive stage.
A Pap Smear is important as early detection of cervical cancer significantly improves the chances of a full recovery.
It is a very well established fact that PAP Smear and HPV screening and protection can significantly reduce mortality and morbidity associated with cervical cancer.
Who Is At Risk of Cervical Cancer?
ALL women who have ever had sexual intercourse are at risk of cervical cancer.
Your risk of cervical cancer is increased if you:
- Early age of sexual debut
- Multiple sexual partners
- Have a weakened immune system
- Smoking
- Other sexually transmitted infections
- Have HPV infection or genital warts
How Often Should A PAP Smear Be Repeated?
A PAP smear should be done at least once every 3 years.
If you are aged 30 years and older, you will be recommended to get a HPV test as well for screening.
How often the test needs to be repeated really depends on the results of your PAP smear or HPV test.
If you have a history of a previous abnormal PAP smear result or HPV infection, you will be required to undergo more regular testing.
The appropriate test and timing will be recommended after consulting with your doctor.
How To Prepare for a PAP Smear?
There are a few things to take note of before you do your PAP Smear.
- Do not do a PAP smear during your menstrual period.
Ensure that your test does not coincide with your menstrual period. It should ideally be at least 1 or 2 weeks after your menstrual period.
- Avoid sexual intercourse before you do your PAP smear
- Do not apply any creams, lubricants or medications in the vaginal area 48 hours before the test.
- Find an experienced female doctor you are comfortable with. A PAP smear can be quite an intimate procedure for a woman, and having an experienced doctor perform the procedure can make the procedure more comfortable and painless for the woman.
- Try to relax as much as possible – tensing up or being nervous will make the PAP smear more uncomfortable.
How Is A PAP Smear Conducted?
A PAP smear usually takes less than 5 minutes to perform. The test itself is very safe and you should expect only very minimal discomfort.
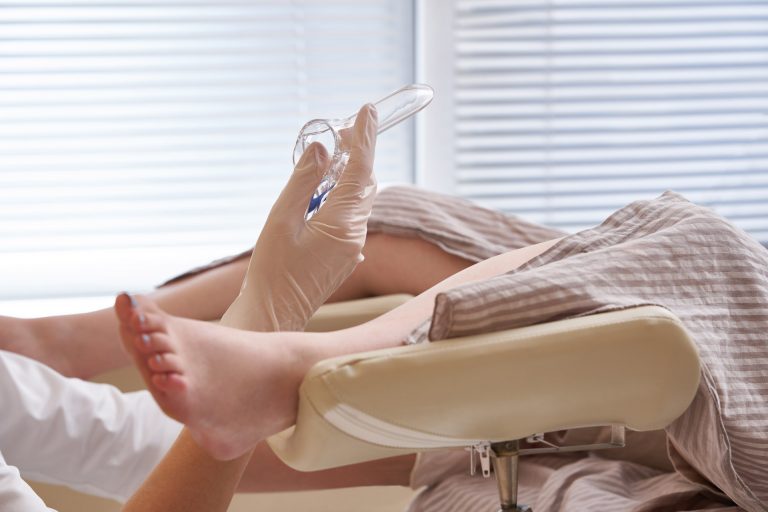
The doctor will first get you to lie on the examination couch with your knees bent and legs apart.
Next, a small plastic device called a vaginal speculum will be inserted into the vagina to help the doctor obtain direct visualization of the cervix.
This part of the procedure may feel slightly uncomfortable.
The doctor will then obtain cells directly from the cervix using a special PAP smear brush
The sample is then sent to the laboratory for analysis. Results will be ready in 1 week.
Many women hold off their PAP smear tests due to previous unpleasant or painful experiences.
However, having an experienced female doctor perform the examination for you will make a big difference in making the process more comfortable and painless.
What Happens After The PAP Smear?
You may expect some vaginal discomfort or mild bleeding right after your PAP smear exam. This is normal not to worry. The bleeding will resolve after a few hours.
Your doctor will then go through the results with you when it is ready. This usually takes about 1 week.
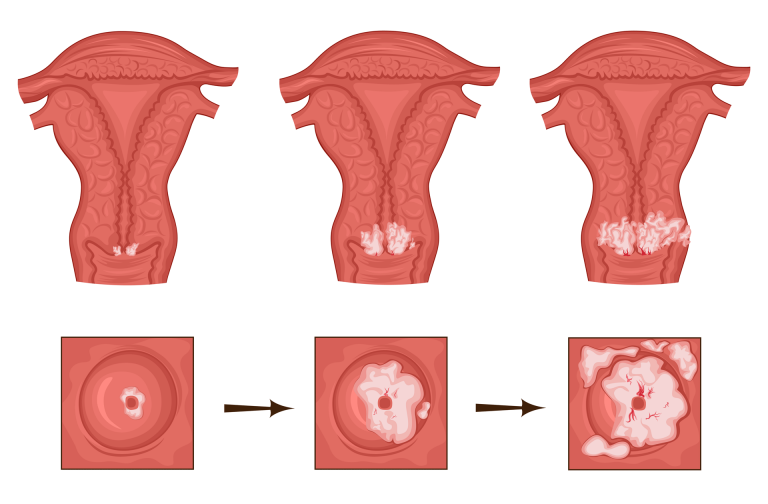
What Happens If You Get An Abnormal PAP Smear Result?
Abnormal results usually fall into 2 main categories – inflammation caused by fungal or bacterial infection, or abnormal precancerous cells that could potentially develop into cervical cancer.
Inflammatory PAP smear
A PAP smear can sometimes occasionally pick up certain fungal or bacterial infections, including an STD known as trichomonas.
Your doctor will usually prescribe a course of antifungal medications or antibiotics to help clear the infection. You may be asked to repeat a PAP smear again in about 6 months.
Abnormal Cells on PAP smear
The primary purpose of performing a PAP smear is for early detection of abnormal precancerous cells.
If abnormal cells are detected on your PAP smear,it is important to ascertain if these abnormal cell changes are associated with a high risk HPV infection.
If only a PAP smear was done, your doctor may advise adding on a HPV test to check for high-risk HPV strains.
This will give us a better idea on how serious the abnormality is.
You will also be referred for a more detailed examination called a colposcopy, which allows your doctor to have a closer look at the cervix. A biopsy may also be taken to check if the cells are truly precancerous.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is recommended for women to get regular PAP smear screening up to the age of 65 years old, only if your previous 3 PAP smear results have been normal consecutively, for the past 10 years.
Women who have a history of abnormal cervical cell changes may be required to continue regular PAP screening past the age of 65 years old, depending on the advice of your doctor.
Some women who have undergone a total hysterectomy (surgery to remove the whole womb and cervix) may also be able to stop PAP smear screening earlier, after the surgery, if the surgery was performed for a benign cause.
There is no risk in getting a PAP smear, as this is an extremely safe procedure.
This is a simple procedure that can be done in less than 5 minutes in a women’s clinic, and can go a long way in cancer prevention for many women out there
Women who have ever had sexual intercourse before will need to begin their PAP smear screening from the age of 25.
This is because cervical cancer is caused by the virus known as the Human Papilloma Virus. ( HPV)
A girl is exposed to HPV only through sexual contact, and hence as long as a girl has had sexual activity before, she will be advised to do a PAP smear for cervical cancer screening.
Girls who have never engaged in any form of sexual intercourse before are not required to do a PAP smear. This is because they would not have any exposure to HPV.
You are still encouraged to take the HPV vaccine even if you are not sexually active.
Cervical cancer is a slow progressing disease and can take a few years to develop. This is why early detection and screening is crucial as it can be cured if detected early.
Yes, you are still required to do a PAP smear even if you have taken the HPV vaccine.
AUTHOR

Dr Michelle Chia
Medical Director
After graduating from the National University of Singapore, Dr Michelle's journey allowed her to train in Women's Health and Aesthetic Medicine. Her experience has led her to be featured on multiple media platforms including Radio Stations and prominent Magazines like Her World, Women's Weekly and CLEO. Her work has also received recognition both locally and internationally in several Medical Conferences.
Ezra Clinic is a Women’s Health, Wellness and Aesthetic Clinic that is conveniently located at the top floor of Royal Square Medical Suites in Novena, Singapore’s Medical Health Hub.
Helmed by Dr Michelle Chia, Ezra Clinic is your chosen one stop clinic for all your Women’s Health and Wellness needs.
Address
101 Irrawaddy Road #21-09, Royal Square Medical Centre, Singapore 329565

